As organisations grapple with the increasing frequency and complexity of cyber threats and the numerous threat actors which are the source of such threats, there is a rising demand for methodologies that proactively manage cyber risk exposure. Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) has emerged as a crucial solution to this challenge. The approach embodies a systematic, ongoing process that effectively identifies, assesses, and addresses the cyber threat landscape for organisations.
However, the implementation of CTEM also comes with distinct challenges. In this article I explores the concept of CTEM, its core objectives, the challenges it faces, and solutions to those challenges.
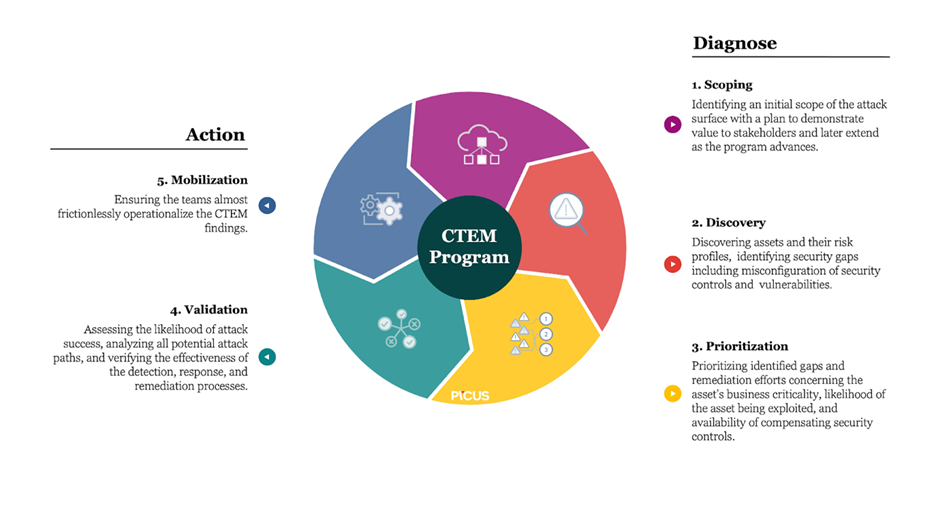
Unpacking Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM)
CTEM represents a significant leap from traditional cybersecurity approaches, which commonly focus on sporadic, one-off assessments of vulnerabilities. Contrarily, CTEM follows a continuous process that persistently scrutinises the threat landscape, identifying new threats, and assessing their potential impact on the organisation’s digital assets.
At its core, CTEM embodies a cyclical process of threat detection, assessment, response, and subsequent improvement. It’s a methodology that goes beyond reactive strategies and aims to stay ahead of the threat curve by ensuring the organisation’s cybersecurity posture is in alignment with the dynamic threat landscape. It’s like a never-ending cycle of vigilant sentinels tirelessly protecting an organisation’s cyber domain if i can borrow a Matrix analogy.
Delving Deeper into the Objectives of CTEM
The objectives of CTEM are multi-faceted and go beyond simply identifying threats. They represent a shift towards a more proactive and efficient approach to cybersecurity.
- Timely Threat Identification: CTEM’s foremost objective is to guarantee the timely identification of threats. By following a continuous approach, organisations can quickly identify emerging threats and respond to them proactively, mitigating the risk of potential attacks.
- Uninterrupted Risk Assessment: CTEM enables a continual understanding of the organisation’s risk profile. By assessing threat exposure continuously, organisations can effectively prioritise responses based on the severity and potential impact of identified threats.
- Proactive Defense Mechanism: Traditional reactive measures often lead to substantial losses. CTEM encourages a proactive approach to cybersecurity, enabling organisations to anticipate and neutralise threats before they even manifest.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: Early identification and mitigation of threats translate into significant savings in incident response costs. CTEM can lead to considerable improvements in operational efficiency by reducing downtime and optimizing resource allocation for incident response.
The Challenges Encountered in Implementing CTEM
Despite its numerous benefits, CTEM is not without its share of challenges. Organisations need to be aware of these to effectively strategize their implementation.
- Resource Intensiveness: CTEM demands considerable resources, both technologically and in human capital. Maintaining a continuous threat management process involves round-the-clock monitoring, assessment, and response, which can be taxing on resources.
- High Complexity: The dynamic nature of the cybersecurity landscape adds complexity to implementing CTEM. New threats, vulnerabilities, and attack methodologies are constantly emerging, demanding continuous learning and expertise.
- Managing False Positives: Dealing with false positives, or benign activities mistakenly flagged as threats, can be a significant challenge. These can inundate security teams and potentially divert attention from real threats.
- Integration Issues with Existing Systems: Integrating CTEM with pre-existing security infrastructure can pose a challenge. It often necessitates substantial adjustments to processes and systems, potentially causing disruptions and consuming valuable time.
Solutions for Overcoming CTEM Challenges
While the challenges associated with CTEM implementation are significant, they are not insurmountable. Here are some potential solutions:
- Effective Resource Management: Organisations can mitigate resource concerns by adopting automation wherever possible. Automated threat detection and response tools can reduce the human capital needed for CTEM and increase efficiency.
- Continuous Training and Education: To tackle the complexity of the evolving cybersecurity landscape, organizations need to invest in ongoing training and education. This should aim to keep the security team abreast of emerging threats, vulnerabilities, and attack methodologies.
- Advanced Threat Detection Tools: False positives can be managed by using advanced threat detection tools that use artificial intelligence and machine learning to distinguish between benign activities and real threats.
- Comprehensive Integration Planning: A well-planned and carefully executed integration plan can mitigate the disruptions caused when introducing CTEM into existing security infrastructure. It’s also crucial to ensure that the integration is done in stages, with sufficient testing at each stage to minimize potential disruptions.
In conclusion, while the challenges are substantial, the benefits that Continuous Threat Exposure Management brings to an organisation’s cybersecurity posture cannot be overlooked. Successful implementation of CTEM can significantly reduce threat exposure and enhance an organisation’s resilience against cyber threats.
GL.iNet MT2500 Mini VPN Security Gateway
#thatcybergirl